Free Equation Solver – Step-by-Step Math Calculator
Free equation calculator solves linear, quadratic, and system of equations from text or image. Includes graphs, roots, and alternate forms.

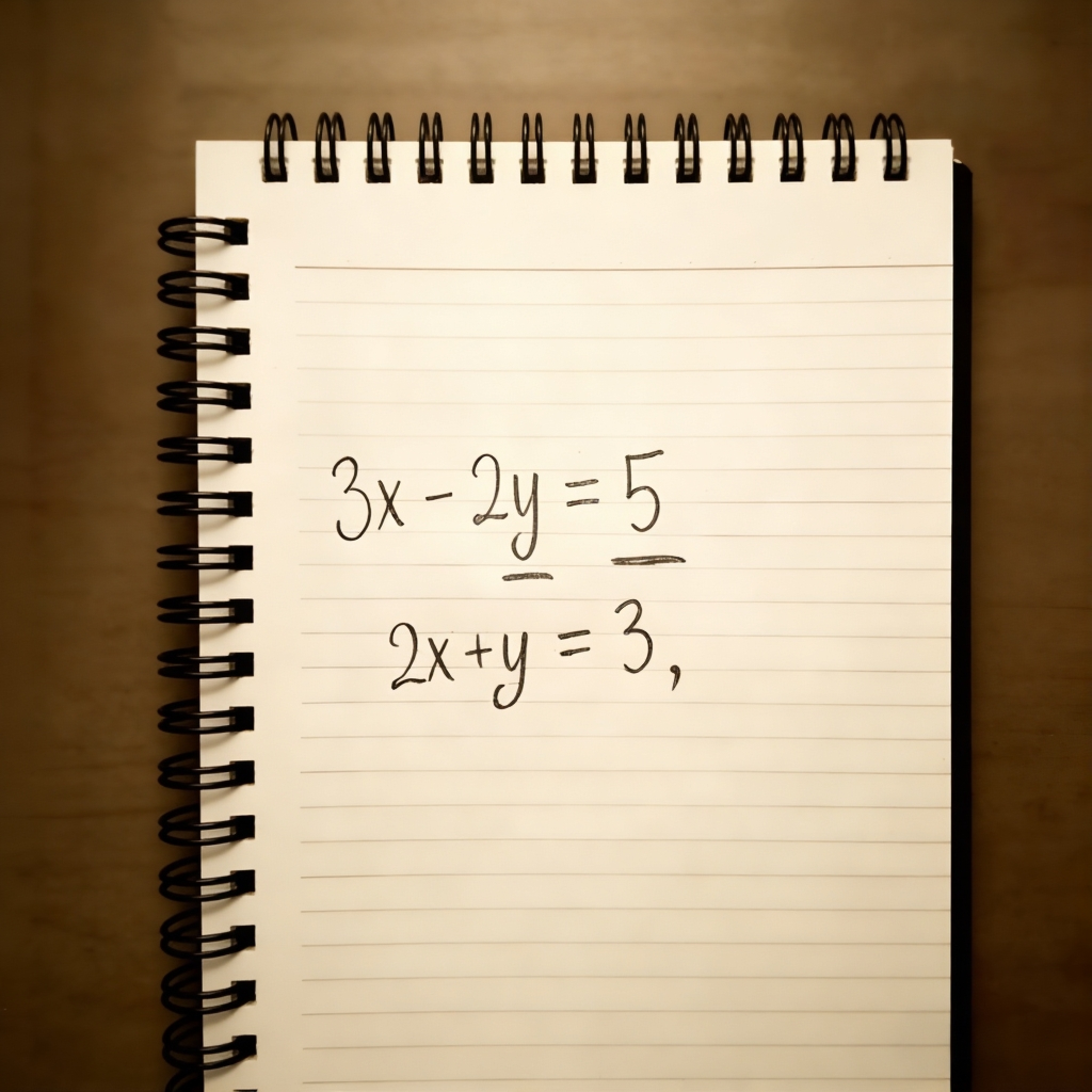

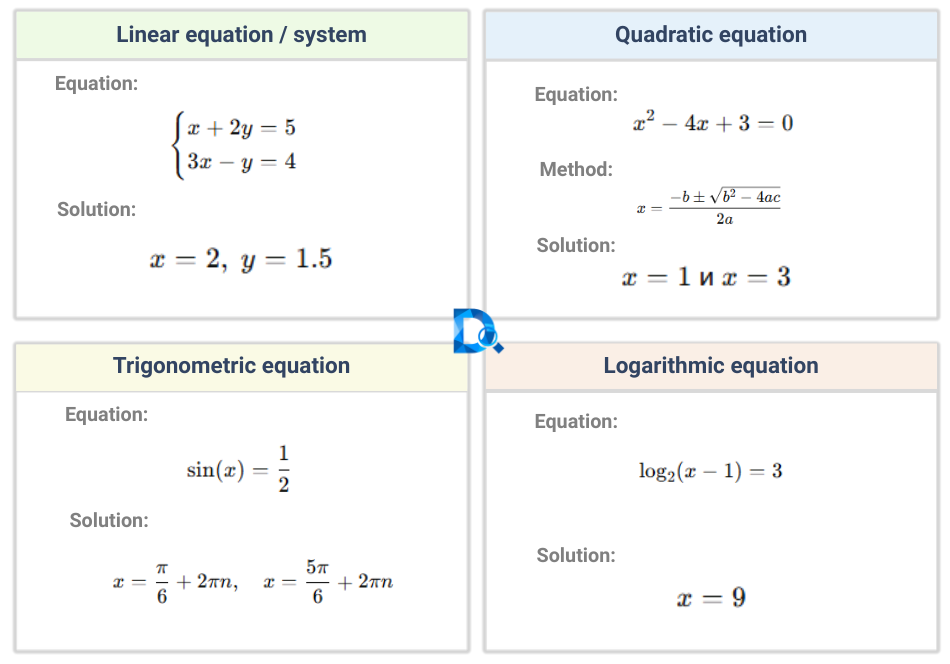
What Is an Equation?
An equation is a mathematical statement containing unknown variables. Solving equations means finding the
values of unknowns by establishing a relationship between known and unknown quantities. Common types of
math equations include linear equations, quadratic equations, trigonometric equations, logarithmic
equations, and cubic equations.
Equations are essential in mathematics, physics, engineering,
and economics. They are powerful tools for solving real-world problems and understanding complex systems.
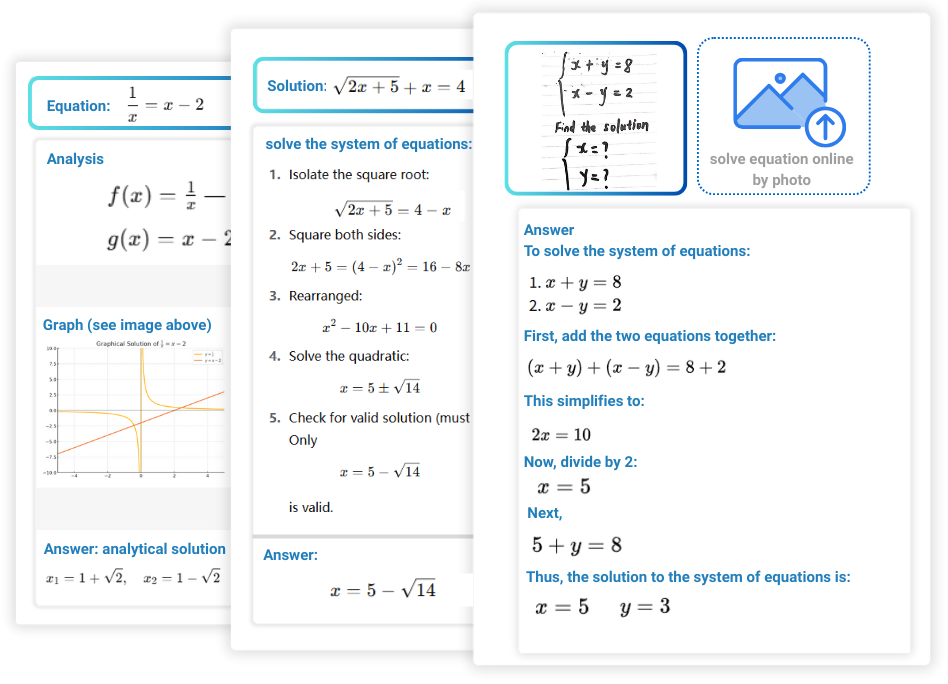
What Is an Equation Calculator?
An equation calculator is an AI-powered tool for solving math equations. It analyzes input using algorithms to quickly and accurately solve various types of equations and systems of equations. Users can type in equations or upload photos containing equations. Decopy AI equation solver will automatically recognize the content, apply standard solving methods, and display the step-by-step solutions.
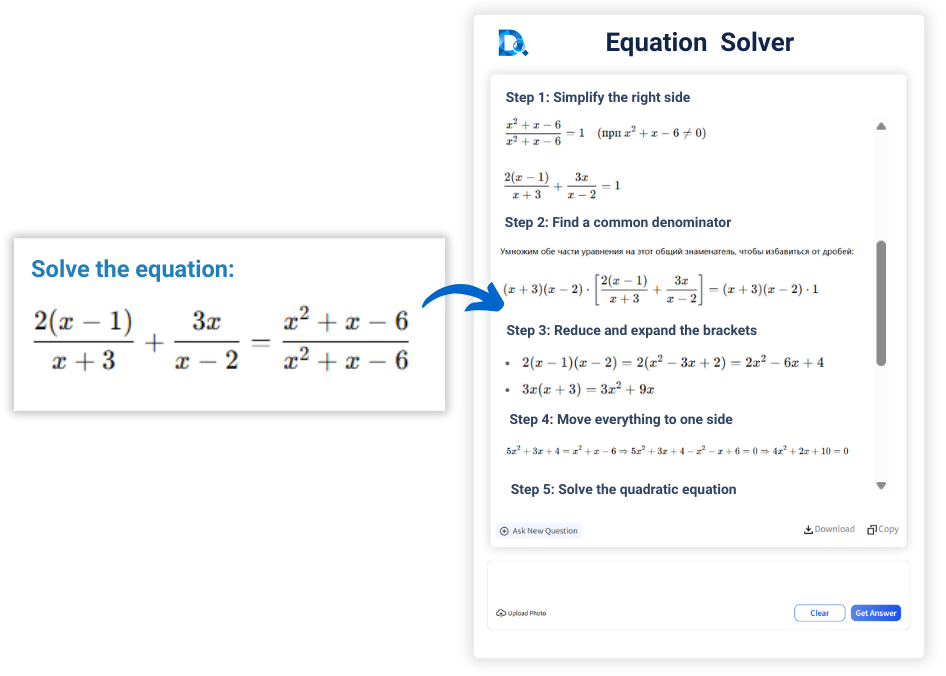
How to Solve Equations?
Traditionally, solving equations requires manual setup, transformations, and calculations, such as
factoring, using the discriminant, or Gaussian elimination. For higher-degree equations or complex
nonlinear systems, more advanced mathematical methods and numerical techniques are needed.
With
an online equation calculator, you can simply upload a photo of the equation or enter it directly. The AI
math equations solver will quickly provide accurate answers. To make the process easier to understand,
Decopy AI equation calculator simulates human solving methods—such as elimination, substitution, or the
quadratic formula—and shows all the step-by-step solutions.
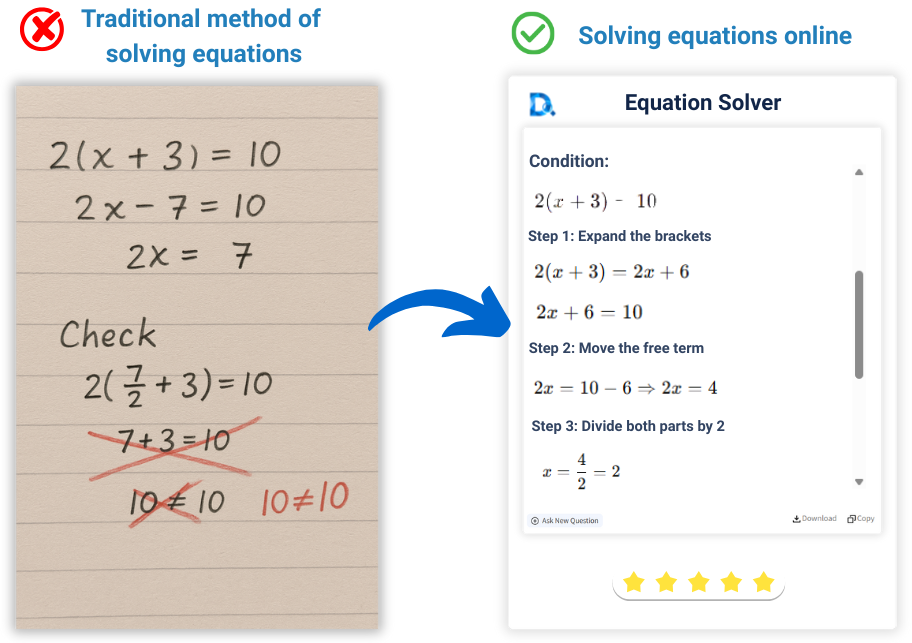
How Does Decopy AI Equation Calculator Work?
Decopy AI equation calculator is powered by an advanced AI math engine that combines algebra, numerical
analysis, and algorithmic optimization.
When users input or upload math equations, the system
automatically detects the equation type (such as linear equations, quadratic equations, trigonometric, or
logarithmic) and selects the best solving method accordingly:
For linear equations and systems
of equations, it uses Gaussian elimination or matrix methods for fast solving.
For quadratic
equations, it applies the discriminant-based quadratic formula for step-by-step solving.
For
trigonometric, logarithmic, and cubic equations, it uses standard transformations, factoring, or numerical
approximations.
For complex nonlinear systems, it applies numerical methods or advanced
solvers.
This equation solver provides final answers and shows step-by-step solutions to help
users understand the mathematical principles.
Features of Equation Calculator
Quickly and accurately solve math equations online using photos or manual input. Supports all types with step-by-step analysis.
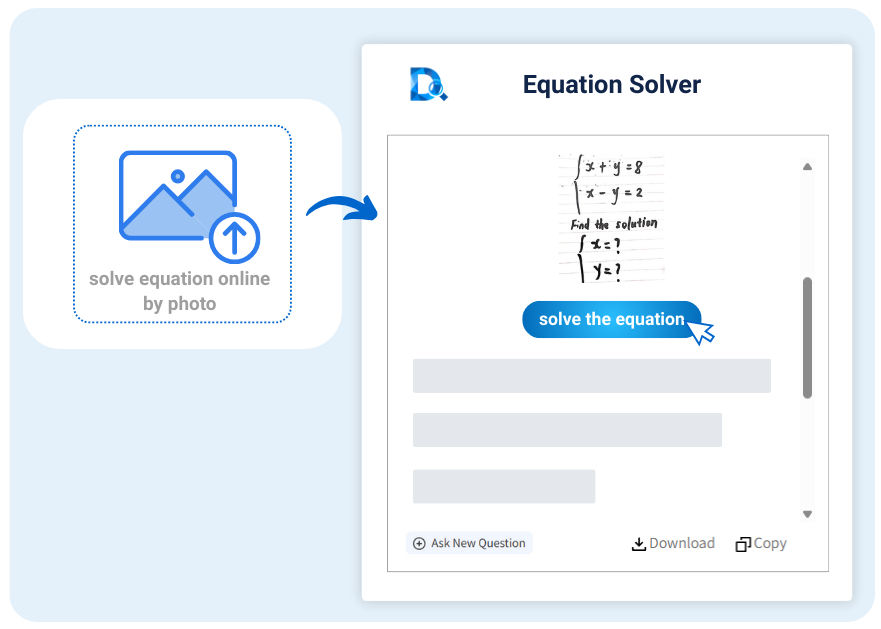
Photo solve
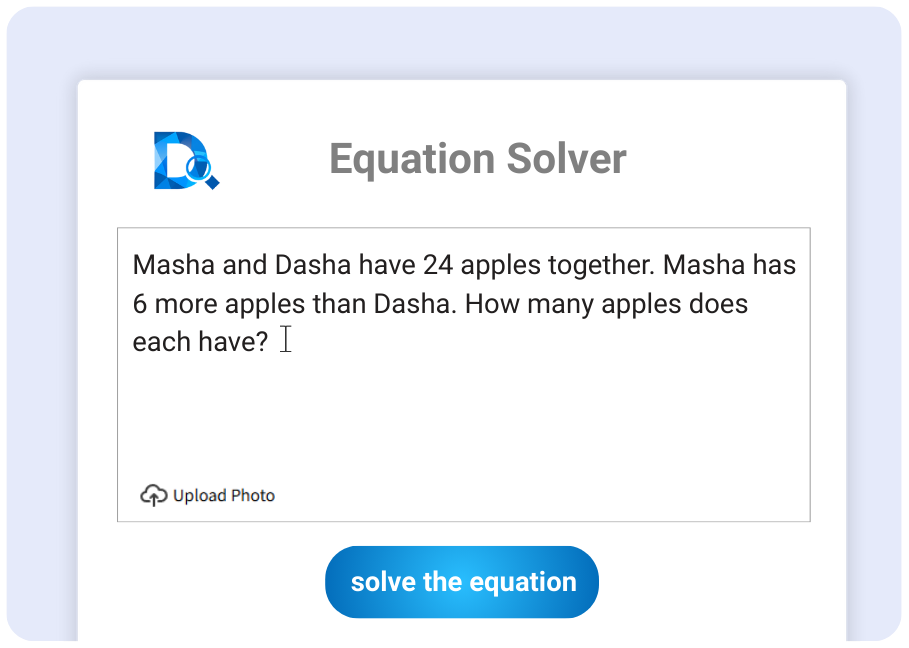
Manual input
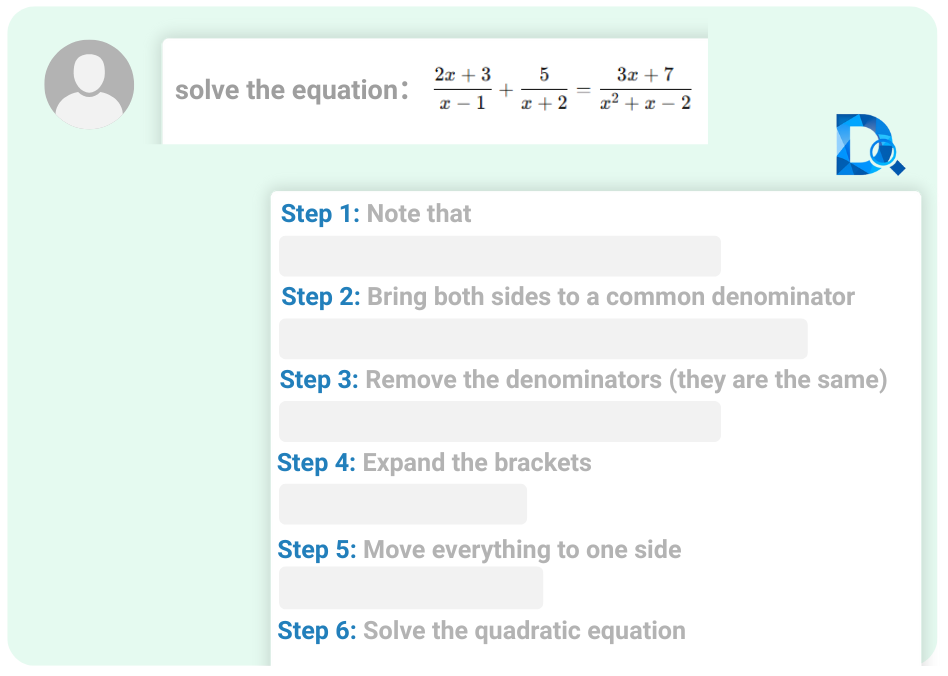
Step-by-Step Solutions
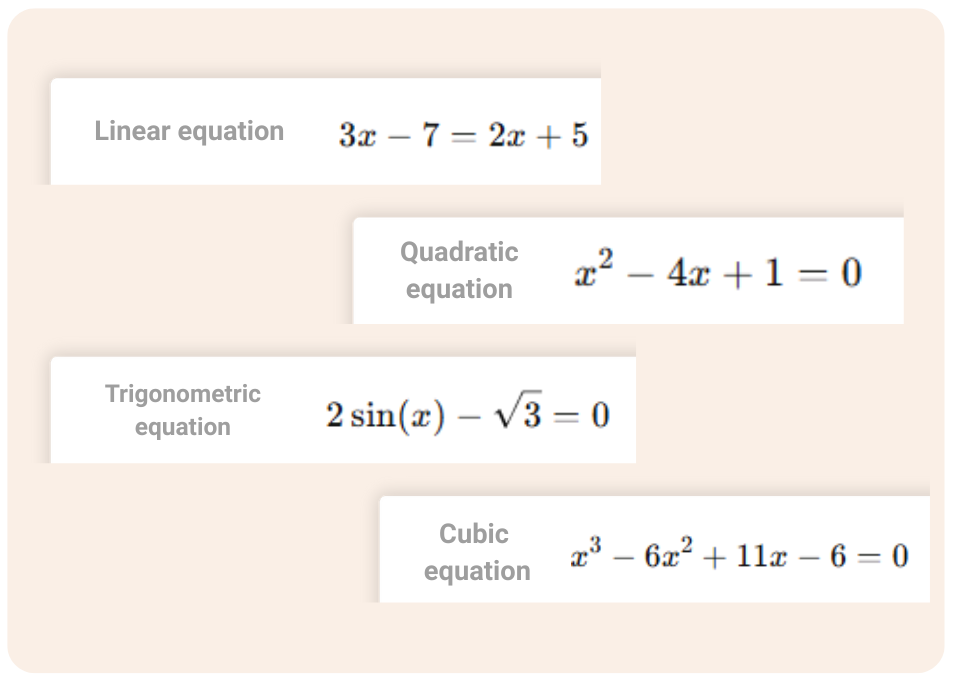
Support for Multiple Equation Types
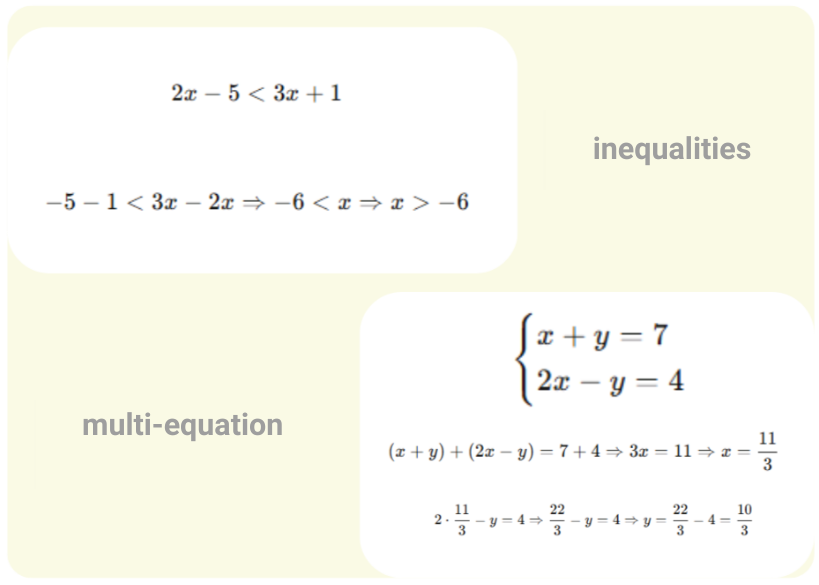
Inequality and System of Equations Solving
Mobile-optimized
A Math Equation Calculator Accessible Anytime,Anywhere
Mobile-friendly online equation calculator supporting photo or manual input with step-by-step analysis.

Student Assignments

Exam Review

Classroom Support

Complex verification

Instructional Grading
Self-Study
Supported Types of Equations
Our equation calculator can solve the following types of math equations. No matter the complexity, you'll get a detailed step-by-step solution.
| Type of Equation | General Form | Solution Features |
|---|---|---|
| Linear equations | ax + b = 0 | One root, solved by rearranging and dividing |
| Quadratic equations | ax² + bx + c = 0 | Quadratic formula, up to two solutions |
| Biquadratic equations | x⁴ + bx² + c = 0 | Solved using variable substitution |
| Polynomial equations | aₙxⁿ + ... + a₀ = 0 | Up to n real or complex roots |
| Logarithmic equations | log_b(f(x)) = g(x) | Solved by rewriting as f(x) = b^g(x) |
| Exponential equations | a^{f(x)} = b^{g(x)} | Logarithmic transformation of both sides |
| Radical equations | √f(x) = g(x) | Square both sides and check domain |
| Absolute value equations | |f(x)| = g(x) | Two cases: f(x)=g(x) and f(x)=–g(x) |
| Trigonometric equations | sin(x), cos(x), ... | Use periodicity and identities |
| Complex equations | f(z) = 0 | Solutions in the complex plane |
| Matrix equations | AX = B | Linear algebra methods, inverse matrices |
| Rational equations | P(x)/Q(x) = 0 | Check domain and find rational roots |
| Floor function equations | ⌊f(x)⌋ = g(x) | Solved within integer intervals |
| Root-based construction | f(x) = (x − r₁)... | Build polynomial from known roots |
| Point-based construction | f(x) through (x₁, y₁)... | Interpolation methods |
| Numerical methods | f(x) = 0 | Approximate root finding (e.g., Newton's method) |
| Differential equations | y', y'' = f(x) | Find function y(x) via solution methods |
How to Use Decopy AI Equation Calculator?
- 1
Open the website and go to equation solver page.
- 2
Upload a photo or directly enter your equation.
- 3
Click "Start Solving" and the system will automatically analyze it.
- 4
View the step-by-step solution or ask follow-up questions.
Why Use Our Equation Calculator
100% Free
no sign-up, no ads, and absolutely no hidden costs. Start solving math equations online instantly.
Accurate and Reliable
Powered by an intelligent algorithm, Decopy AI equation solver precisely handles all types of math equations.
Simple and Effective
Even beginners can easily solve math equations using the math equation calculator.
Multilingual Support
This math equation calculator recognizes math equations in 8 different languages, making it suitable for international exams.
No Download Required
Equation calculator works directly in your browser and does not require app installation.
Support for All Types of Equations
Solves core types of equations and systems (linear equations, quadratic equations, trigonometric equations, and more).
What our customers are saying
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Different types of math equations online require different solving approaches:
Substitution method
– used for solving systems of equations with two variables;
Elimination method – applied to
remove variables and obtain a particular solution;
Completing the square / root formula –
suitable for solving quadratic equations;
Graphical or numerical methods – applicable to
higher-degree equations or those lacking an analytical solution;
Equation calculator – ideal for
quickly solving structurally complex or time consuming equations, while also providing a detailed,
step-by-step solution process.
The method of completing the square is a technique for solving quadratic equations of the form
𝑎𝑥² + 𝑏𝑥
+ 𝑐 = 0.
It involves transforming the expression into a perfect square form, such as
(𝑥 + 𝑑)² =
𝑒,
which makes the equation easier to solve visually. This method is particularly useful when solving
quadratic equations where the coefficients are difficult to handle using standard solving methods.
The most important rule in solving equations online is maintaining balance between an equation's left and
right sides.
Whatever operation you perform on one side, addition, subtraction, multiplication, or
division—you must do the same on the other side. Otherwise, the fundamental principle of the equation as an
equality is violated, and the result of solving one equation will be incorrect.
The steps are as follows:
1. Move terms: Transfer the unknowns to one side of an equation and
the constants to the other side.
2. Simplify: Combine like terms and simplify the expression.
3. Solve:
Use addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division to reduce the equation to the form 𝑥 = value. Always
ensure that each operation is applied to both sides of the equation simultaneously when solving equations
online.
Simplifying is a basic operation in solving equations and usually includes:
1. Removing parentheses;
2.
Combining like terms (e.g., 3x + 2x = 5x);
3. Following the order of operations (PEMDAS: Parentheses →
Exponents → Multiplication/Division → Addition/Subtraction) to make the math equation cleaner and easier for
solving equations online.
1. Simplify both sides: Combine like terms and expand parentheses.
2. Isolate the variable:
Move all terms containing the variable to one side.
3. Find the value of the variable:
Use inverse operations to simplify coefficients and find the final result.
Simply enter a math equation online, this equation solver automatically recognizes variables and structure, using intelligent algorithms (such as algebraic transformations, numerical methods, and others) to solve equations online. It then displays step-by-step solutions with justifications for each stage. This is ideal for learning, checking math homework, or verifying complex examples.
📘 Full List of Supported Math Functions
Explore the syntax and notations you can use in Decopy AI equation calculator.
📂 Click to view supported functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| abs(x) | Absolute value of x |
| arccos(x) | Arccosine of x |
| arccosh(x) | Hyperbolic arccosine |
| arcsin(x) | Arcsine of x |
| arcsinh(x) | Hyperbolic arcsine |
| arctg(x) | Arctangent of x |
| arctgh(x) | Hyperbolic arctangent |
| asec(x) | Arcsecant of x |
| asech(x) | Hyperbolic arcsecant |
| cbrt(x) | Cube root of x |
| ceiling(x) | Round up to nearest integer |
| chi(x) | Hyperbolic cosine integral |
| cos(x) | Cosine of x |
| cosh(x) | Hyperbolic cosine |
| cosec(x), csc(x) | Cosecant of x |
| ctg(x) | Cotangent of x |
| diracdelta(x) | Dirac delta function |
| e | Euler's number ≈ 2.71828 |
| exp(x) | Exponential function (e^x) |
| factorial(x), x! | Factorial of x |
| floor(x) | Round down to nearest integer |
| gamma(x) | Gamma function |
| heaviside(x) | Heaviside step function |
| i | Imaginary unit (√-1) |
| lambertw(x) | Lambert W function |
| ln(x), log(x) | Natural logarithm |
| log(a,x) | Logarithm with base a |
| oo | Infinity |
| pi | Pi ≈ 3.14159 |
| sec(x) | Secant of x |
| sech(x) | Hyperbolic secant |
| sign(x) | Sign of a number |
| sin(x) | Sine of x |
| sinh(x) | Hyperbolic sine |
| sqrt(x) | Square root |
| sqr(x), 𝑥² | Square of x |
| Si(x), Ci(x), Shi(x), Chi(x) | Integral trigonometric and hyperbolic functions |
| tg(x), tan(x) | Tangent |
| tgh(x) | Hyperbolic tangent |
| x + y, x - y | Addition, subtraction |
| x * y, x / y | Multiplication, division |
| x^n, pow(x,n) | Exponentiation |





