How to Organize and Summarize Literature
When doing research, everyone reads a large amount of literature, but after reading, have you ever experienced the frustration of "I've read similar literature that could be useful, but I can't find it now"? The purpose of reading literature is not just to get through it, but to be able to use it. This requires us to organize and summarize the literature we've read. While it's easier said than done, how should we approach this task? The author has summarized some key points that will hopefully help fellow researchers.
First, it's important to understand that the software you use or the method you choose is not the key factor affecting your reading effectiveness! You've probably heard about and may even be using various document management tools through various channels, but tools are just tools. More important than how to use tools is how to change your mindset about organizing literature. The author recommends a "four-step" approach: first reading through the PDF, then organizing horizontally using Excel, then summarizing vertically using Word, deepening your impression and clarifying the literature's context through multiple readings from different angles. Finally, archive everything using your preferred literature management tool, or simply save it in categorized folders if you don't have one!
Additionally, during the literature organization process, you can use Decopy AI's AI Summarizer tool to summarize literature, which can greatly speed up the efficiency of literature organization! AI Summarizer can automatically and accurately extract the core content of literature. The global overview can deeply summarize content and supports multi-language processing, helping researchers quickly understand the core content of non-native language literature. Users can choose from five dimensions: global overview, core viewpoints, structured summary, key insights, or common questions for summarization, reducing repeated reading and improving efficiency.

Literature Organization - Four Easy Steps
Step One: PDF Reading - Screening and Annotation
The method of reading papers doesn't need much explanation - choose between intensive and extensive reading based on the paper's quality and relevance, look for valuable points in the literature, which could be an argument, a method, data, or a theory, and mark them all during reading for later organization. When you encounter a brilliant argument, make sure to mark it specially, as I'm sure everyone has experienced the frustration of wanting to cite a brilliant argument but being unable to find it again. Most importantly, you need to have a clear boundary or standard while reading: which literature needs to be summarized. Because not every piece of literature needs to be summarized. From literature retrieval to the final literature that needs to be read, there is a full process of screening, and the literature that reaches the summarization stage is actually relatively few. I hope we can reach a consensus on this point because summarizing massive amounts of literature is almost impossible for us (excluding bibliometric analysis). We need and must screen quickly by browsing abstracts, keywords, introductions, and conclusions based on our research topics. If we don't screen and blindly start summarizing, it will definitely be twice the effort for half the result.

Reading Tips:
Combine Intensive and Extensive Reading: Choose between intensive or extensive reading based on the literature's quality and relevance. For literature highly relevant to your research topic, intensive reading is recommended; for background or reference literature, you can quickly browse through the abstract, keywords, introduction, and conclusion.
Mark Key Information: During reading, promptly mark valuable points in the literature, such as:
Important arguments or theories
Research methods or experimental designs
Key data or results
Connections to your own research
Special Marking of Highlights: When you encounter brilliant arguments or methods, be sure to mark them specially. Many people often face the embarrassing situation of "remembering a certain viewpoint but unable to find its source" when writing later - marking in advance can effectively avoid this problem.
Screening Criteria:
Relevance: Does the literature directly support or contradict your research question?
Innovation: Does the literature propose new theories, methods, or findings?
Authority: Is the literature published in high-quality journals? Are the authors authorities in the field?
Through screening, the amount of literature that needs to be summarized will be greatly reduced, thus avoiding getting lost in massive amounts of literature.
Step Two: Horizontal Organization - Systematic Recording Using Excel
What is horizontal? Horizontal refers to comparing the existing forms of things that coexist in space simultaneously. Horizontal organization is a broad grasp of the literature you've already read, used to record which literature you've read and what the general information about these pieces of literature is, such as source, author, title, topic, keywords, etc. The editor recommends the most common and widely used Excel, but if you have any good tools, feel free to recommend them in the comments! Based on the key points you've already marked in the literature during reading, organize them categorically in Excel. The specific organization methods and key points naturally vary from person to person, but generally should clearly mark: 1. The source of the literature, including title, author, year, journal, because organizing this information can better understand the overview of the field and will affect whether to cite this literature later; 2. The overview of the literature, including keywords (self-defined), abstract (select main content from abstract), objective (self-extracted). 3. Literature highlights, including main connections to your own paper and any noteworthy points (key points) 4. Literature conclusions, if summarized in figures that would be best, paste the figures into Excel for a clear view of the article.
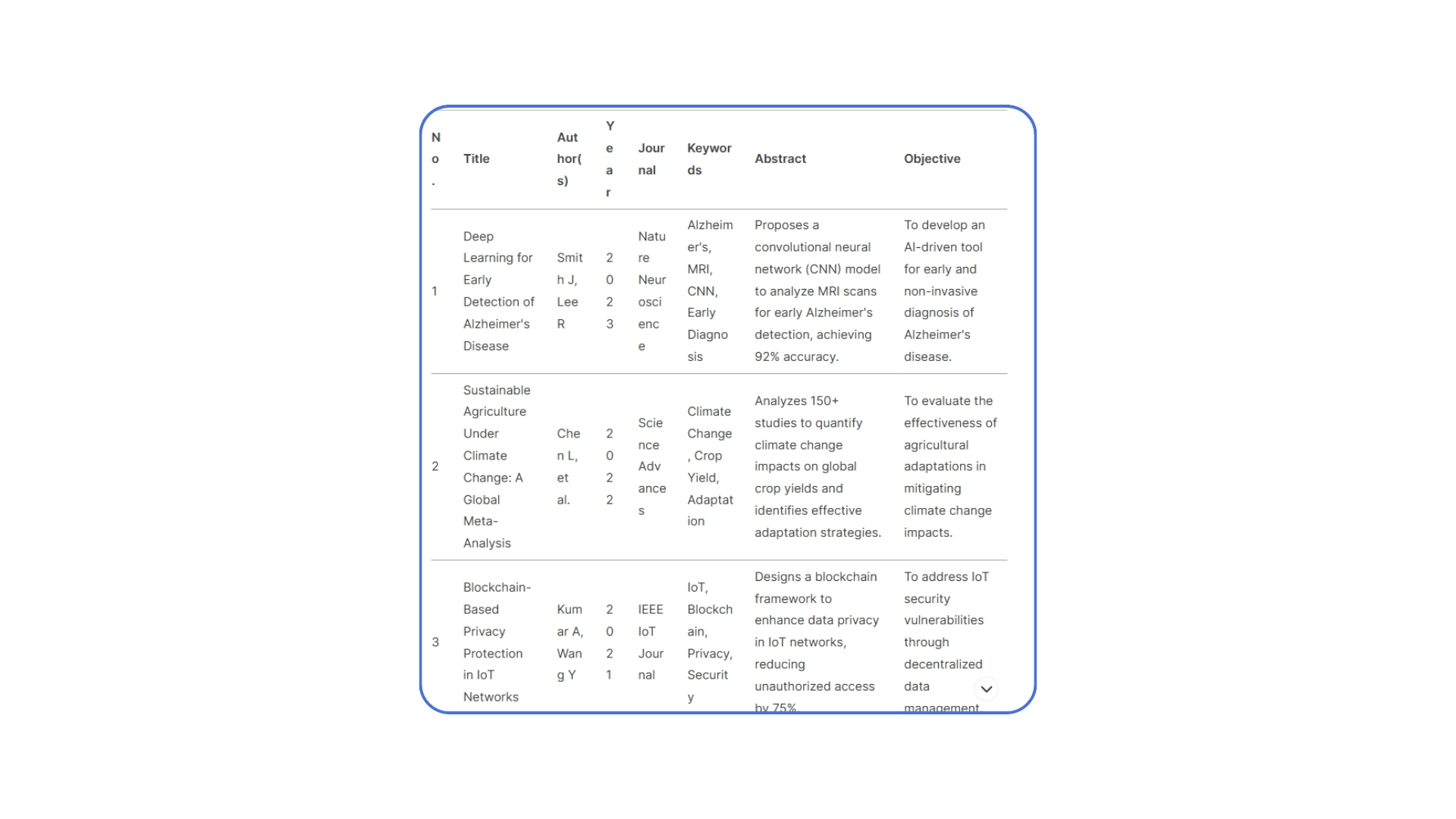
Organization Content:
1. Basic Literature Information:
Title
Author
Publication Year
Journal Name
DOI or Link (for quick access to original text)
2. Literature Overview:
Keywords: Can be self-defined for later retrieval.
Abstract: Extract core content from the abstract.
Research Objective: Extract the research purpose in your own words.
3. Literature Highlights:
Main connections to your own research.
Noteworthy points (Key Points): Such as unique research methods, important data support, innovative theoretical frameworks, etc.
4. Literature Conclusions:
Summarize the main conclusions of the literature in concise language.
If there are important figures or tables in the literature, you can screenshot and paste them into Excel for intuitive understanding.
Organization Tips:
Categorize: Classify literature according to research topics or keywords.
Regular Updates: Update the Excel sheet promptly after reading new literature to avoid omissions.
Through horizontal organization, you can quickly understand the core content of each piece of literature and lay the foundation for subsequent vertical summarization.
Step Three: Vertical Organization - Using Word to Summarize Literature Connections
Vertical comparison is comparing the state of a single thing with its past or future state. Here, vertical organization refers to finding connections between different articles, confirming development relationships, or clarifying future citation scenarios, or summarizing by topic categorically (because in our research and learning process, we definitely won't just look at articles in one direction). To put it more simply, it's summarizing the key points and results organized in Excel. In simple terms, it's finding connections between different literature and putting related points together, thus finding vertical connections in a pile of literature, extracting similar research themes and mutually supporting or contradicting research findings that run through different literature, linking independent literature together. I hope everyone will soon experience the satisfaction of thinking of one and finding a group when needed later.
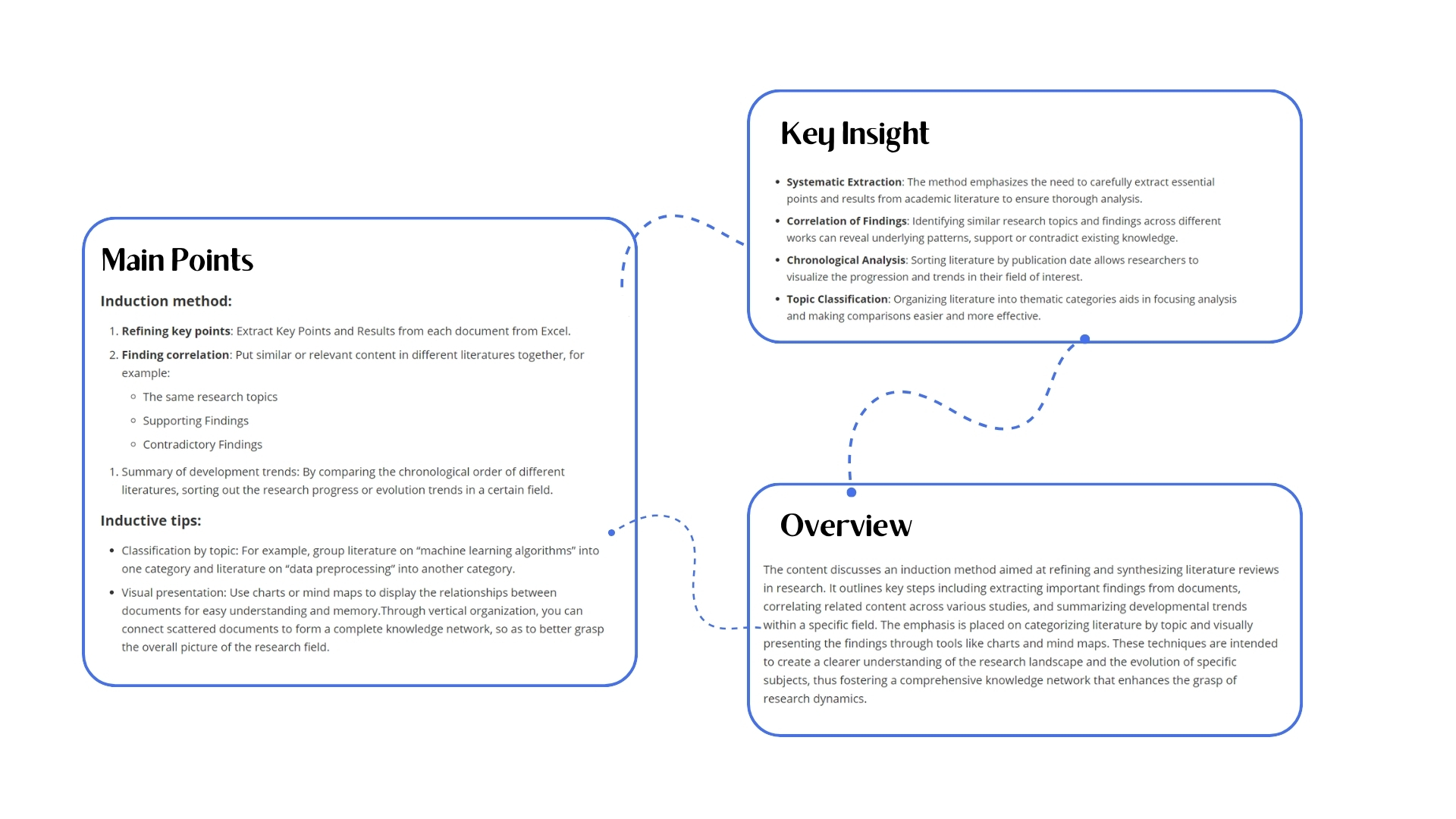
Summarization Methods:
Extract Key Points: Extract Key Points and Results from each piece of literature in Excel.
Find Connections: Put similar or related content from different literature together, for example:
- Similar Research Themes - Supporting Findings - Contradictory FindingsSummarize Development Trends: Through comparing the chronological order of different literature, sort out the research progress or evolution trends in a field.
Summarization Tips:
Categorize by Topic: For example, categorize literature about "machine learning algorithms" as one category, and literature about "data preprocessing" as another category.
Visual Presentation: Use charts or mind maps to show relationships between literature for better understanding and memory.
Through vertical organization, you can link scattered literature together to form a complete knowledge network, thus better grasping the full picture of the research field.
Step Four: Literature Management - Efficient Archiving Using Tools
For regular use, the previous three steps are basically enough, because the themes, research ideas, research results, and other content we need most have already been summarized in horizontal and vertical organization. However, there are always situations that require us to read the original text, and at this time, quickly finding and starting to read articles requires us to further manage the literature we've read. These several quite useful software, such as Endnote, Mendeley, are recommended for everyone to use~
Recommended Tools:
Endnote: Powerful functionality, suitable for managing large amounts of literature, supports multiple citation formats.
Mendeley: Free and easy to use, supports PDF annotation and cloud synchronization.
Zotero: Open-source tool, supports web capture and team collaboration.
Management Tips:
Categorized Storage: Categorize literature according to research topics or projects.
Add Tags: Add keywords or tags to each piece of literature for quick retrieval.
Regular Backup: Back up the literature library to the cloud or external hard drive to prevent data loss.
Literature Summarization - Using Decopy AI Intelligent Summarization
In research work, literature summarization is an indispensable skill. It's not only a window to understand the current status of the research field but also an important tool for providing theoretical support and inspiration for subsequent research. Whether writing papers, designing experiments, or applying for projects, literature summarization plays a crucial role. Through systematic literature summarization, researchers can quickly grasp the research progress, hot issues, and future trends in a field, thus laying a solid foundation for their own research.
So what are some useful methods for literature summarization? Let the author tell you one by one. First, we need to screen literature, selecting high-quality, highly relevant literature based on research topics. You can quickly judge the value of literature by reading abstracts, keywords, and conclusions. The next step is to extract key information. This is where Decopy AI's AI Summarizer function comes into play, quickly extracting key information and generating summaries through Decopy AI's AI Summarizer function. At this time, you don't need to manually record, you just need to focus on research background, problems, methods, results, and innovations, all of which will be covered when AI Summarizer summarizes.
Then, classify and organize the extracted information by topic, method, or chronological order for subsequent analysis. Don't worry, with the help of AI Summarizer, these will all be very easy. Based on the classification and organization, extract commonalities and differences between different literature, summarize research status, trends, and gaps. Present the summarized content in text form, usually including introduction, main body, and conclusion. Literature summarization is now complete!
Advantages of Using Decopy AI
Improve Efficiency: AI Summarizer can quickly process large amounts of literature, saving time on manual reading and information extraction.
Enhance Accuracy: AI Summarizer can accurately extract the core content of literature, reducing omissions and errors in manual extraction.
Support Multiple Languages: AI Summarizer supports multi-language processing, helping researchers quickly understand the core content of non-native language literature.
AI Summarizer Features and Tutorial
AI Summarizer is a free and efficient text summary generation tool where users can quickly extract core content from text through simple operations. When using this tool, first choose a suitable summary mode, such as global overview, core viewpoints, structured summary, key insights, or common questions, then directly paste text or upload files in the text box, with the system supporting a maximum input of 200,000 characters. Users can set output language and summary length according to their needs, and after clicking the "Summarize" button, the generated summary will be displayed in the area below. If humanized text is needed, the "Humanize Text" function can be used to adjust the language style. The generated summary can be directly copied or downloaded and saved, while the "Clear" button is used to clear current content to start over. This tool is particularly suitable for processing long texts such as papers, reports, or news, meeting diverse needs through flexible configuration and significantly improving information organization efficiency.
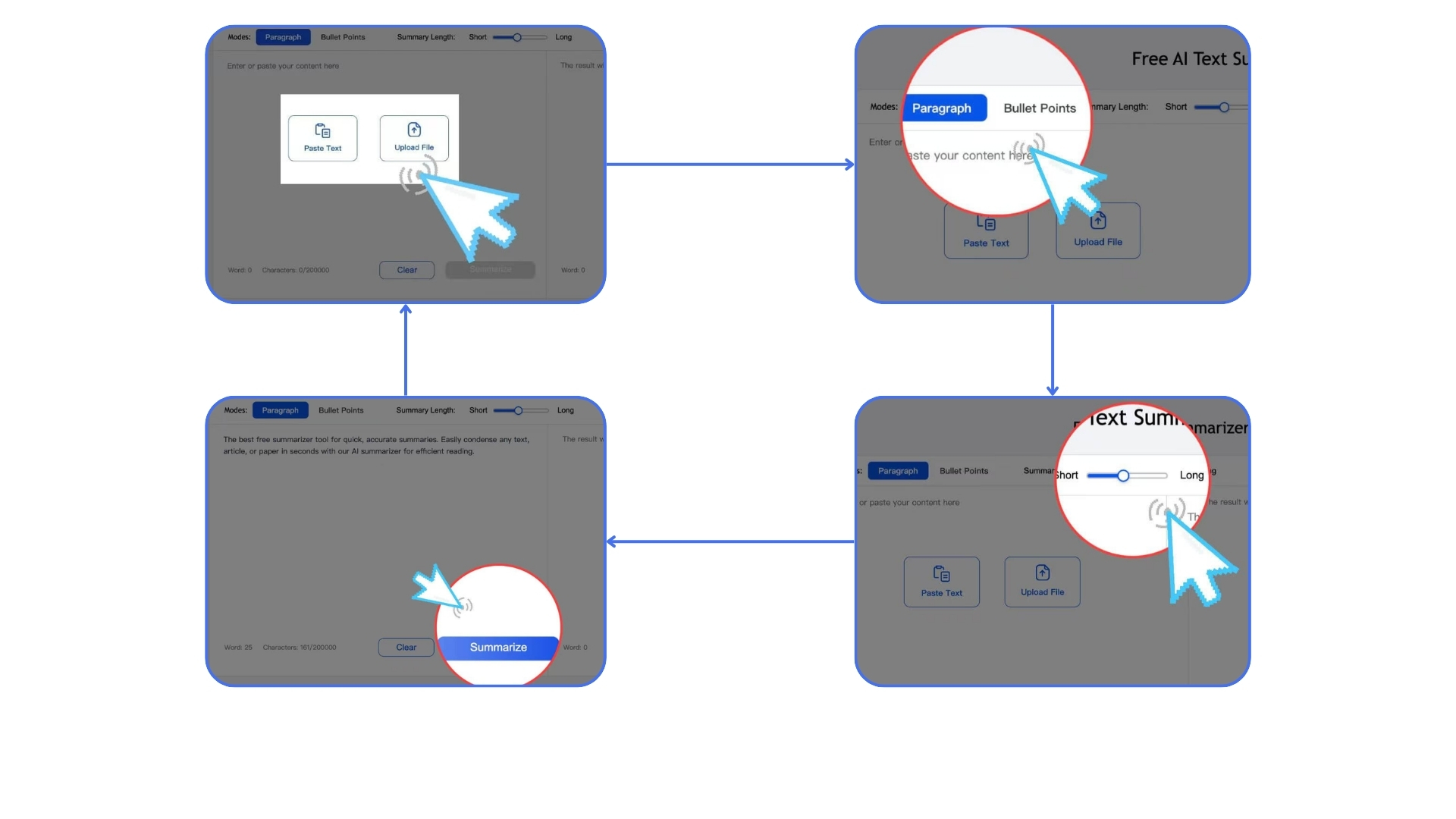
Examples of Using AI Summarizer
Using AI Summarizer for literature summarization can significantly improve research efficiency, especially suitable for handling massive amounts of literature. Researchers can first manually import collected literature into the tool, and AI Summarizer will automatically extract the core content of each piece of literature (such as research background, methods, results, and conclusions) and generate concise summaries, helping to quickly screen out high-quality literature highly relevant to the topic. For screened literature, the tool can further extract keywords, at which point readers can manually generate topic tags (such as "machine learning" or "medical diagnosis"), showing research trends through charts, providing an initial framework for subsequent classification and organization.
However, it should be noted that AI-generated summaries may have information bias or be too superficial, so human intervention is indispensable - researchers need to combine their own understanding of the field to supplement details, correct classification tags, and deeply analyze connections between literature (such as comparing contradictory conclusions from different studies, sorting out the development context of the field), and finally write a complete report with rigorous logic and critical thinking based on the AI-generated summary framework. This mode of "AI efficient processing + manual deep processing" can both avoid getting lost in the sea of literature and ensure the accuracy and academic value of the summary content, particularly suitable for integration analysis of multilingual literature or interdisciplinary research.
Below is the introduction part of a paper written by the author, which contains some key information such as research background, research methods, research results, and conclusions. Through Decopy AI's AI Summarizer function, the author quickly extracted key information and generated a concise summary, helping the author quickly understand the research status, trends, and gaps.

The core of literature organization and summarization lies in thoughts and methods, not the tools themselves. Through the "four-step" method - PDF reading, Excel horizontal organization, Word vertical summarization, tool management, and with the help of the Decopy AI summarization tool, you can deeply understand literature from different angles, thoroughly summarize literature, and establish a systematic literature knowledge base. This method not only improves the efficiency of literature reading but also provides strong support for subsequent research and writing. Hope the sharing in this blog can help everyone navigate their research path more easily!